The species of mosquito that transmits Zika is the same as the mosquito that transmits Dengue, Chikungunya and Yellow Fever.2
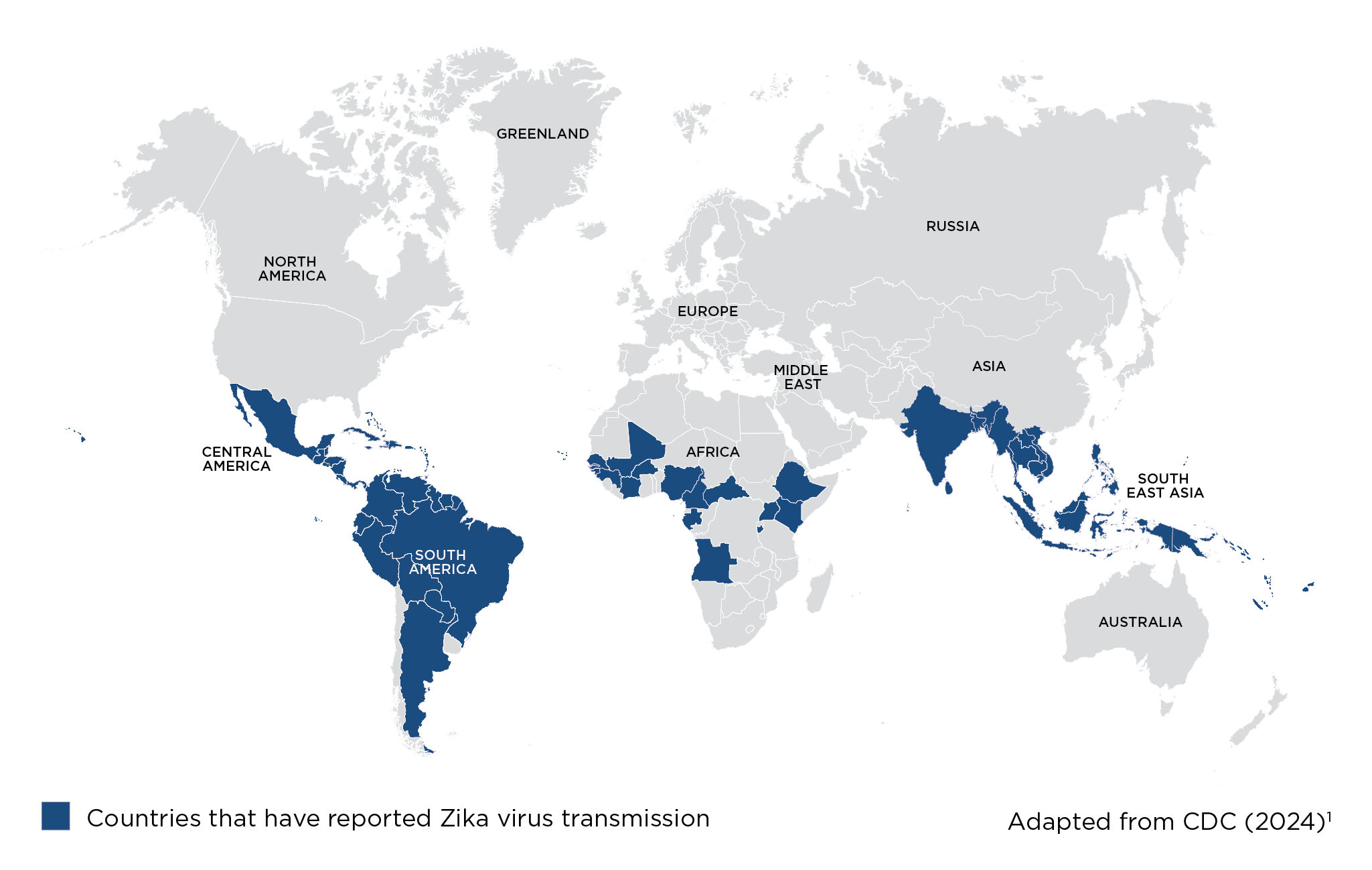
Risk areas for Zika
FAQs
-
Key fact
-
How do you get Zika virus?
By being bitten by infected mosquitoes which carry the virus. The disease can also be caught through sex with an infected partner or from mother to baby during pregnancy.2
-
Which countries are affected by Zika virus?
Many countries in the Pacific region, South and Central America, the Caribbean, parts of Africa, and parts of south and southeast Asia (see map).1
-
What are the symptoms of Zika virus?
Most people do not develop symptoms. If present, they may appear between 3-14 days and are generally mild. They can last 2-7 days and include fever, rash, conjunctivitis, muscle pain, joint pain, feeling of being generally unwell, and headache.2
-
How serious is Zika virus?
Some babies born to women who become infected can have severely abnormal brain development. Possible links with a range of other complications are being investigated.2
-
Can I prevent getting Zika virus?
You can take the following precautions to help reduce your risk of infection:
- Visit your nearest convenient pharmacy or specialist travel health clinic for a risk assessment before your trip
- If pregnant or intending to become pregnant women should take extra care to avoid being bitten, and try to avoid becoming pregnant while travelling and for 3 months afterwards3
- Use a recommended insect repellent containing either Picaridin, DEET, PMD or OLE (oil of lemon eucalyptus), IR3535 or 2-undecanone4
- Wear appropriate clothing (e.g. loose fitting long-sleeved clothes, long trousers, socks and shoes) to minimise exposed skin5,6
- Use insecticide-treated mosquito nets if you are sleeping or resting in accommodation without air conditioning or sleeping outdoors during the day or night5
- Practise safer sex (including using condoms)2
Ready to get started? Check now for your nearest travel health clinic.
Get friendly advice from the UK's largest network of travel clinics*.
* This list is not exhaustive and other travel health providers are available.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Countries & Territories at Risk for Zika. February 2025. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/zika/geo/index.html (Last accessed May 2025)
- World Health Organization. Factsheet. Zika Virus. December 2022. Available at: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/zika-virus (Last accessed May 2025)
- NHS. Conditions A to Z. Zika. February 2022. Available online: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/zika/ (Last accessed May 2025)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Yellow Book 2026. Environmental Hazards and Risks. Mosquitoes, Ticks, and Other Arthropods. April 2025. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/yellow-book/hcp/environmental-hazards-risks/mosquitoes-ticks-and-other-arthropods.html (Last accessed May 2025)
- UK Health Security Agency. Mosquito bite avoidance: advice for travellers. January 2023. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/mosquito-bite-avoidance-for-travellers (Last accessed May 2025)
- Fit for Travel. General Travel Health Advice. Mosquito Bite Avoidance. Available online: https://www.fitfortravel.nhs.uk/advice/malaria/mosquito-bite-avoidance (Last accessed May 2025)
UK-BOTB-2500026 May 2025
